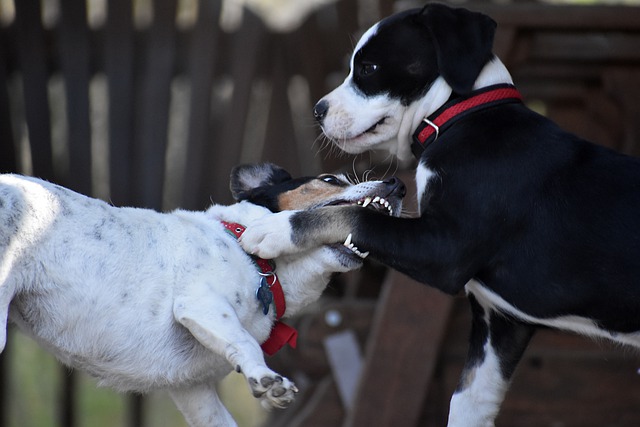
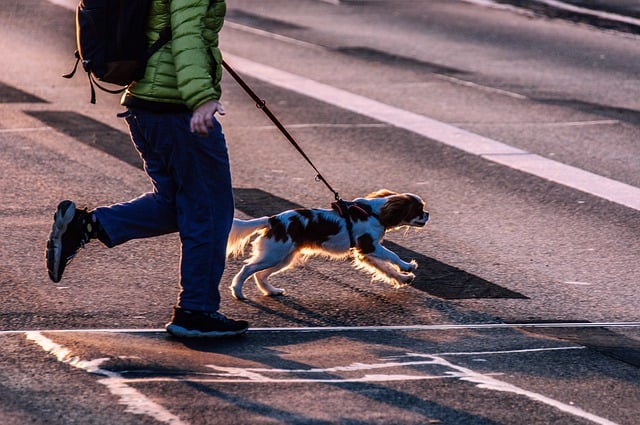
A dog owner needs to recognize the signs of aggression before it’s too late. If your puppy or dog is showing signs of aggression, has been aggressive, or think he might become aggressive, it’s important to take the time to assess what’s making him aggressive.
If you carefully observe his behavior throughout the day, you will learn a lot about what may be causing him to misbehave. Below are the major classifications of aggressive dog behavior. You must identify the true reason or source of the aggression so that you can take appropriate action to stop your dog’s aggression.
Aggression caused by fear
This occurs when a dog is very frightened but cannot escape the situation due to fear. In this situation, the dog’s most likely reaction is to attack. For example, a dog that is being chased and cornered by pound personnel will bite out of fear. This type of aggression can also occur when a dog is physically punished.
The amount of punishment a dog can take without being frightened varies, so each dog will react differently to punishment. Keep in mind that if a dog reacts aggressively to punishment, it is because it is afraid or in pain (another type of aggression we will discuss later).
On the other hand, dogs that have not been properly socialized may show fear and aggression when they are in unfamiliar situations. A dog that has not been socialized with children may attack because of the fear it feels when threatened by a child who tries to cuddle it.
Territorial aggression
In this type of aggression, the dog attacks to keep any stranger away from its territory. This is a particular type of aggression for possession of their resources. For example, your dog may react very aggressively if you approach him while he is eating. He may also react in the same way when he is guarding toys. Puppies are not as territorial as older dogs… however, territorial behavior in puppies usually appears when they reach adulthood.
Abusive aggression (bullying)
This type of aggression can be seen in an insecure dog towards dogs that are physically or psychologically weak. It is a type of aggression frequently displayed by dogs with high social status towards other weaker dogs.
This type of aggression has nothing to do with dominance, as some might think, but is due to the aggressive behavior being self-reinforcing. Anthropomorphism is similar to the bullying that often occurs in schools, where some children or teenagers physically or psychologically abuse other students.
Although it may seem wrong from a human perspective, it is useful within the canine family (as long as it is not overdone) for puppies to learn to give signals of appeasement and submission. In this way, they learn to cope with aggressive situations without relying on brute force and thus avoid physical harm. In general, this type of aggression manifests itself in behavioral manifestations and rarely results in physical harm.
Possession of resources
This type of aggression is similar to territorial aggression. Some trainers, behaviorists, and veterinarians confuse it with dominance aggression, but it is not the same thing. Aggression for possession of resources tends to occur in varying degrees. First, there are the warning signals, then come to the final stages that end in biting.
You can see that a dog is defending something at the time of the aggression, such as food, a toy, or a specific space. This is why you see male dogs fighting over a female… Possession of resources. This type of aggression can occur in both dominant and submissive dogs and should not be attributed solely to dominance.
Maternal aggression
This form of aggression is very common in all mammals and other animals and has a very strong insensitive basis. It occurs when the mother attacks to defend her puppies. This type of aggression occurs when the mother is afraid that her pups will die or be injured.
Therefore, the female must be in a situation that does not pose problems that could trigger maternal aggression. The best way to deal with this type of aggression is to manipulate the environment to avoid situations that are stressful to the female. The mother and puppies will be calm and there will be no reason for any aggression.
Aggression caused by pain
Pain is the cause of many dog attacks that have no apparent reason. A toothache, inflammation, hip dysplasia, and many other conditions can cause your dog to react aggressively. If your dog suddenly becomes aggressive, the aggression may be caused by pain. If this is the case, the first thing to do to solve the problem is to go to the veterinarian for the proper diagnosis.
Delayed or redirected aggression
Displaced aggression occurs when the dog tries to attack something or someone furiously, but a physical barrier prevents it from doing so. In this situation, frustration causes the dog to redirect its attack to other dogs, people, or objects. This type of aggression is relatively common in dogs that live behind a fence or cannot get out.
It is also very common in dogs that are on a leash. It is also seen in dogs that go out on a leash, but have never been properly socialized. When they try to attack other dogs, they are controlled by their owners. If the leash is too short or the owner is holding the dog by its collar, the aggression may be redirected to the owner.
Aggression due to physiological changes
Physiological changes caused by illness, age, or changes in the dog’s environment can cause aggression. Diseases that cause this type of aggression do not cause pain. For example, if your dog is gradually losing his eyesight, he will often be startled by people or dogs approaching him.
Because of his visual impairment, he reacts by running away or attacking. In addition, the passage of time also causes physiological changes that can lead to aggression. In addition, changes in the environment can also cause physiological changes leading to aggression. In some cases, for example, the dog’s diet may increase or decrease the animal’s predisposition to aggression.
Predator aggression
Predatory aggression is the result of the release of the dog’s hunting instincts. It occurs when the movement of something that simulates pursued prey triggers the dog’s aggression. This aggression is usually directed at young children, joggers, bicycles, small dogs, and other small animals.
It is a movement that triggers the natural predatory patterns that exist in every dog. Also included in this type of aggression is social facilitation aggression. It occurs when one or more dogs are associated with the initial attack. For example, a dog attacks a cyclist and other dogs in the vicinity join in the attack even though they initially did not react to the cyclist’s presence.
Dominance aggression or status aggression
Dominance aggression, also known as status aggression, occurs when a dog believes it is the leader of the family and fights to maintain and establish its status in the hierarchy. The dog concludes that it is the supreme leader of the pack and will defend it appropriately. This is an evolutionarily stable strategy that is common to many species.
The bottom line is this. If your puppy or dog shows signs of aggression, don’t ignore it. Get help immediately before you, your pet, or anyone else gets hurt. I know that many of you love your pets dearly and would therefore do what is in the best interest of your pet.